What is Inflation Caused By, and How Do We Stop It?
Inflation is a term used more often than ever in todays world. The economy today is much different than it was 100 years ago, and inflation is a bigger factor than it was then.
The value of the American dollar just seems to continue going down, and many people wonder, “why?”.
What is Inflation?
Inflation is a measure of rising prices in the economy. This can be because of cost-pull inflation, or demand-pull inflation. Inflation leads to higher prices on basic necessities, causing a bigger gap between the rich and the poor.
- Inflation measures rising prices of products and services in an economy.
- When production costs rise, so does inflation. This includes materials, wages, and commodities.
- When demand rises on a product, inflation rises because consumers are willing to pay more for the product.
- Natural disasters can cause inflation by taking out important production sites for a temporary time.
- It is possible for companies to reap the rewards of inflation if they can charge a higher price for their products as a result of an increase in demand.
Picture this: A balloon can be pumped up to just the right amount, and it will lose air overtime. But if you were to consistently put a little bit of air in it anytime it starts to lose a small amount, it would stay at that perfect size.

However, if you pump up the balloon too much, it will burst, and everything is then ruined. That is essentially the Federal Reserve’s job. They are pumping money into the economy, they just have to figure out— how much is too little? How much is too much?
What is Inflation Caused By?
Inflation is caused by a multitude of factors, hence why it has been a problem for the entirety of our lives. To understand what inflation is caused by, we need to understand what the three types of inflation are:
- Cost-Pull Inflation
- Demand-Pull Inflation
- Built-In Inflation
Cost-Pull Inflation: Signs of a possible cost-push inflation:
- Rising Commodity Prices
- Increased Wages
- Production Shortage
1. Rising Commodity Prices :Commodities are major production materials, so if the price of a commodity goes up, so as oil or copper, then the price of a product will naturally increase.
2. Increased Wages :Wages are typically the biggest expense for businesses. When the economy is strong, and unemployment rate is low, there can be a shortage in workers. In turn, companies oftentimes increase wages to attract qualified candidates, which raises the production costs for the company.
3. Production Shortage: If a fire rips through Florida, then there will nost likely be a shortage of oranges. When there is less supply of a product with the same demand as before, the price naturally rises. When prices are higher, this causes inflation.
A company with the ability to create a monopoly is also a contributor to cost-push inflation. It controls the entire supply of a good or service, meaning they have the power to push the price up depending how necessary the good or service is. The Sherman Anti-Trust Act outlawed monopolies in 1890.
Demand-Pull Inflation: Demand pull-inflation is when the demand is higher than the supply. This causes inflation because when the demand is greater than the equilibrium, the price of the product will naturally increase. Consumer confidence tends to be high when the economy is strong and unemployment is at low levels, which leads to higher wages, and more spending. As the demand for a product increases, supply decreases, and then people are willing to pay more to obtain the good.
When people are willing to pay more to obtain a good, the result is higher prices.
One example of demand-pull inflation is oil. The demand for oil has increased drastically over the last few decades, but oil is a scarce resource. Since the amount of oil is limited, but the demand rises, the price of oil goes up. That is why a barrel of oil costs almost three times as much today as it did twenty years ago.
Built-In Inflation: Built-in inflation represents the expectations of future inflations. Basically, when prices rise, workers expect rising wages as well to maintain their cost of living. However, higher wages result in higher cost of production, which leads to higher prices once again. This is what macroeconomists refer to as the Wage-Price Spiral.
The Wage-Price Spiral is a theory formed by macroeconomists to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between rising wages and rising prices. The theory suggests that higher wages would increase disposable income, which heightens the demand for products and causes prices to rise along with the wages. As prices rise, the demand for higher wages continues to grow, which leads to higher production costs, leading to higher prices, and the spiral continues.
Essentially, what the spiral causes, is that your money can buy the exact same amount of product, you just have more paper. The downside, is that any savings you had before is cut lower and lower. Any cash you had stored continues to be worth less and less as the spiral continues.
This is why most economists disagree with higher wages, because it would send the economy into a downward spiral (as it already has) and America would still have the same problem as before.
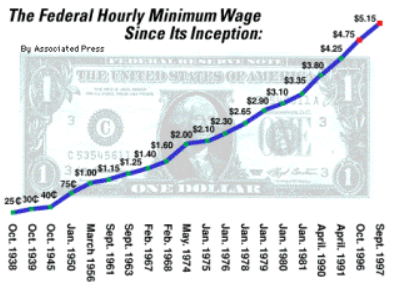
The minimum wage haas steadily increased overtime. It is much higher now than it was in 1997, and we still have the same problem. Has higher wages fixed the problem? Absolutely not.
How Do Economists Measure Inflation?
Economists measure primarily measure inflation with two tools:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Producer Price Index (PPI)
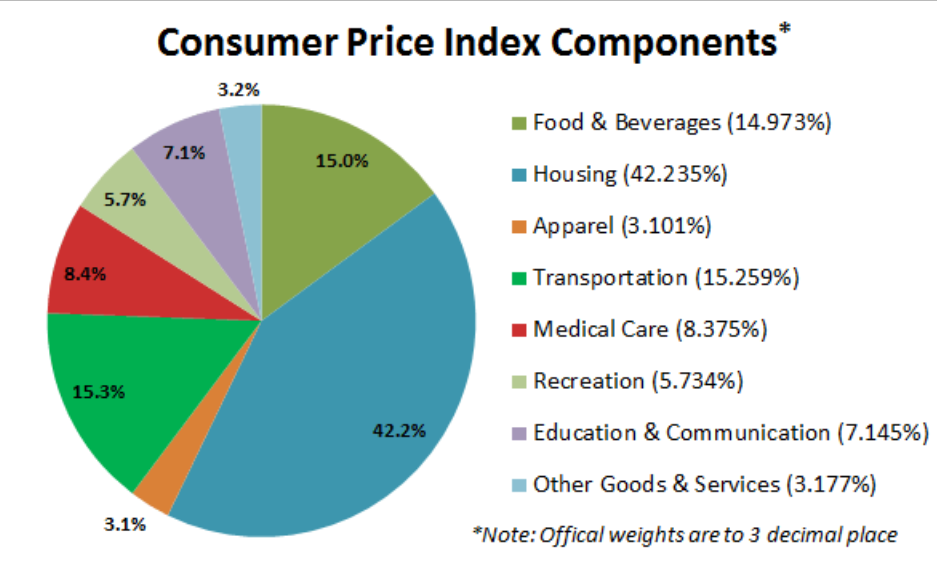
The Consumer Price Index measures the different prices for products and services in our economy.

The Producer Price Index reports the price changes that affect producers. This index is for products like oil, fuel, chemicals, steel, and other commodities. If the price in one of these items is increased, then the increased price will be passed along to consumers, and will affect the price in other products as well.
Is America at Risk?
I’ll tell you how we can keep the problem going: Do what we’re doing right now.
The Federal Reserve is printing money like it’s their hobby, and America is at risk of hyperinflation occurring in the future. An example of hyperinflation is Venezuela, who did this between 2013 and 2019. It created hyperinflation, and the money became worthless. People began using eggs as currency.
Why is Inflation Worse Today Than It was Before?
The Expansionary Fiscal Policy is the expansion of the money supply through deficit spending. Deficit spending pumps money into certain segments of the economy, and creates demand-pull inflation in that area. It delays the offsetting taxes and adds it to the debt.
The money supply is not just cash, but also loans, mortgages, and credit. When the money supply expands, the value of the American dollar decreases. When the dollar declines relative to the value of foreign currencies, import prices rise, thus increasing prices in the economy.
In 1913, a gallon of milk costed about 36 cents per gallon. Move forward one hundred years, and the same gallon of milk costs $3.53 per gallon. That is a straightforward example of inflation in action.
This increase is not due to milk becoming more scarce, or more expensive to make. In fact, the opposite is true. Instead, this price reflects the gradual decrease in the value of money as a result of inflation.
What is Deflation?
A great example of deflation is the Great Depression, during which the cost of goods fell because people did not have access to money or credit due to unemployment, the stock market crash, and other factors.
What is Hyperinflation?
Hyperinflation is when the government prints too much cash, and when too much cash is in circulation, it causes the money to become virtually worthless because everyone has massive amounts of it. As mentioned before, this happened in Venezuela between 2013 and 2019, when they printed off massive amounts of cash.
What is a Liquidity Trap?
A liquidity trap occurs when there is a lot of cash in circulation that is not spent or invested. Instead, people and institutions “hoard” their money. This is a problem because that hoarded money isn’t boosting the economy and creating jobs by being in circulation.
What Major Events Were Caused by Inflation?
- The Great Depression: I’m sure you’ve heard of the roaring 20’s. There was a lot of wild speculation, and more lending than there had ever been before. There were a range of factors that caused inflation during the 20s, but all of this spending led to the biggest burst in history in 1929, when the market crashed. Ben Bernanke, Chairman of the Fed, theorized that deflation during the Great Depression reduced the value of people’s assets. Since people used those assets for collateral, banks were dealing with greater risk and foreclosed on the loans.
In Bernanke’s view, deflation results in a hinderance in the cycle of lending and borrowing that is essential for moving the economy forward.
- The 1970s: Printing money isn’t all bad. It is a way for the Fed to strengthen the economy when it needs to. However, by printing money, the Fed also increases inflation rates, which leads to rising interest rates. Rising interest rates cause the economy to slow down, because there are a lower amount of people taking loans. In the 70s, America was printing money inaccurately, and ended up printing far more than GDP growth represented. Since the GDP grew slowly, and the Fed continued to print money, the value of the American dollar decreased a lot in the 1970s.
- The Great Recession: If the economy enters a liquidity trap, like what happened during the Great Recession, then printing money is no longer a viable option. When the country entered a liquidity trap and people began hoarding money out of fear, the Fed tried to print money to solve the problem. However, people hoarded this money as well, instead of allowing it to circulate in the economy. This led to large increases in the money supply, but only a miniscule difference in price.
Inflation can be a blessing, or a curse. The economy only needs a little bit of money to be pumped every year to match growth of the GDP, any more than that is inflation that hurts the economy.


Interesting article have bookmarked this for the future reference, maybe because I have quite an interest in this topic. Thanks for sharing
Jason 🙂